Unleashing the Power of High Protein, Low Carb Diets, A Comprehensive Guide

In recent years, high protein, low carb diets have gained significant popularity among health enthusiasts, athletes, and individuals looking to shed excess weight. This dietary approach involves reducing carbohydrate intake while increasing protein consumption, leading to a range of potential health benefits.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the science, benefits, food choices, and potential risks associated with a high protein, low carb diet.
1. Understanding High Protein, Low Carb Diets
A high protein, low carb diet is a nutritional strategy that emphasizes consuming a higher proportion of protein-rich foods while minimizing carbohydrate intake. By limiting carbs, the body is prompted to enter a state of ketosis, where it primarily relies on stored fat for energy instead of carbohydrates. This metabolic shift has been linked to various health benefits, including weight loss, improved blood sugar control, increased satiety, and enhanced muscle growth and recovery.
2. Benefits of High Protein, Low Carb Diets
- Effective Weight Loss: High protein, low carb diets are renowned for their ability to facilitate weight loss. Protein has a high thermic effect, meaning it requires more energy to digest, leading to increased calorie expenditure. Additionally, protein-rich foods help promote feelings of fullness and reduce cravings, ultimately reducing overall calorie intake.
- Blood Sugar Control: Restricting carbohydrate intake can stabilize blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. By reducing the consumption of refined carbs, blood sugar spikes and subsequent crashes can be minimized.
- Increased Muscle Mass and Strength: Protein is essential for muscle repair, growth, and maintenance. By consuming an adequate amount of protein, individuals following a high protein, low carb diet can optimize muscle protein synthesis, leading to increased muscle mass and strength gains. This is particularly valuable for athletes and individuals engaged in resistance training.
- Enhanced Satiation: Protein-rich foods are known to be more satiating than carbohydrates or fats. By prioritizing protein in your diet, you can feel fuller for longer periods, which can aid in reducing overall calorie intake and controlling hunger.
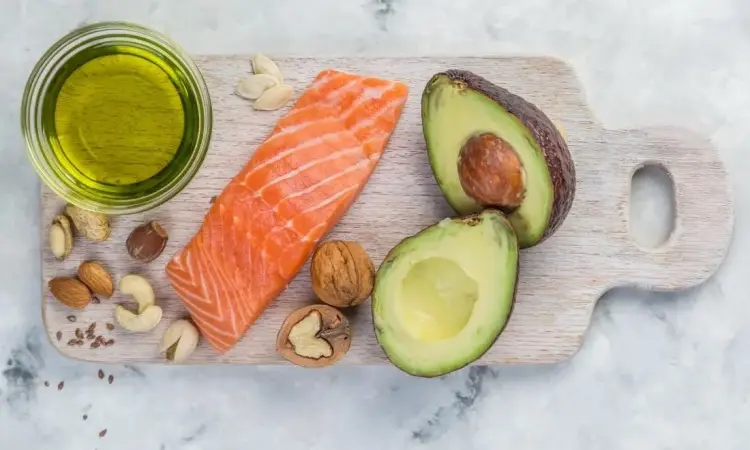
3. Food Choices for a High Protein, Low Carb Diet
- Lean Meats and Poultry: Chicken breast, turkey, lean cuts of beef, and pork are excellent sources of protein with minimal carbohydrates. Opt for skinless cuts and prepare them through grilling, baking, or broiling methods to minimize added fats.
- Fish and Seafood: Fish like salmon, tuna, mackerel, and trout are not only rich in protein but also provide omega-3 fatty acids, which have numerous health benefits. Shellfish such as shrimp, mussels, and oysters are also protein-packed options.
- Eggs: Eggs are a versatile and affordable source of high-quality protein. They are low in carbs and can be prepared in various ways, making them a convenient choice for a high protein, low carb diet.
- Dairy Products: Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, and whey protein are excellent options for those seeking protein-rich dairy sources with minimal carbs. They also contain essential nutrients like calcium and vitamin D.
- Plant-Based Proteins: For vegetarians and vegans, incorporating plant-based protein sources like tofu, tempeh, lentils, quinoa, chickpeas, and edamame can provide ample protein while keeping carb intake low.
4. Potential Risks and Considerations
While high protein, low carb diets offer numerous benefits, there are a few factors to consider:
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Reducing carb intake may lead to a decreased consumption of certain vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber. It is important to compensate by including a variety of nutrient-dense, low-carb vegetables and considering supplementation if necessary.
- Ketosis and Ketoacidosis: Ketosis is a natural metabolic state associated with low carb diets, but it should not be confused with ketoacidosis, a dangerous condition primarily seen in individuals with uncontrolled type 1 diabetes. If you have any underlying health conditions, consult a healthcare professional before starting a high protein, low carb diet.
- Sustainability: The sustainability of a high protein, low carb diet depends on individual preferences and lifestyle factors. Long-term adherence may be challenging for some, so it’s important to find a balance that is enjoyable and sustainable in the long run.
Conclusion
A high protein, low carb diet can be an effective strategy for weight loss, blood sugar control, and muscle growth. By choosing protein-rich foods and minimizing carbohydrate intake, individuals can achieve numerous health benefits.
However, it is essential to consider individual needs, consult with healthcare professionals if necessary, and maintain a balanced approach to nutrition and overall wellbeing. Remember, everyone’s dietary needs and preferences differ, so finding a sustainable eating plan that works for you is key.